PaaS, IaaS, SaaS
What is PaaS, IaaS, SaaS?
What is PaaS?
Platform as a Service (PaaS) is a cloud computing model that provides developers with a platform to build, deploy, and manage applications without infrastructure management. It provides developers with an integrated environment that includes development tools, runtime environments, and deployment resources in the cloud, allowing developers to focus on coding and application logic rather than dealing with the underlying infrastructure.
Features and Benefits of PaaS
PaaS offers several key features and benefits that make it a compelling choice for developers and businesses:
Rapid Development
PaaS provides pre-configured development environments and ready-to-use tools, reducing the setup time required for development. This enables developers to accelerate application development and time-to-market.
Scalability and Flexibility
PaaS platforms offer seamless scalability, allowing applications to handle increased traffic and user demand without requiring manual intervention. It also provides flexibility to scale resources up or down based on application needs.
Collaboration and Teamwork
PaaS enables collaboration among development teams, allowing multiple developers to work on the same project simultaneously.
Automated Deployment and Management
PaaS automates the deployment and management of applications, handling tasks like provisioning servers, configuring databases, and managing security. This automation speed up the development process and lowers operational cost.
Cost Savings
It operates on a pay-as-you-go approach, where you only pay for the resources you use, making it cost-effective for enterprises of all sizes.
Use Cases and Industries that can Benefit from PaaS
PaaS is functional in a variety of sectors and application scenarios. Some typical situations in which PaaS can be helpful include.
Web Application Development
PaaS simplifies the development and deployment of web applications, allowing developers to focus on building user-friendly interfaces and business logic.
Mobile App Development
PaaS provides development frameworks, tools, and backend services that streamline the creation of mobile applications for different platforms.
API Development and Integration
PaaS offers tools and services for developing, managing, and integrating APIs, enabling businesses to expose their services and data securely.
Data Analytics and AI
PaaS platforms often provide integrated data analytics and AI services, empowering businesses to process and derive insights from large datasets.
Internet of Things (IoT)
PaaS offers IoT-specific features, such as device management, data ingestion, and analytics, facilitating the development of IoT applications and services.
Popular PaaS Providers
Several PaaS suppliers provide solid platforms with many features and capabilities. Some well-known PaaS vendors are as follows:
Yuan Jhen Information introduces a cutting-edge DevOps PaaS platform, fostering seamless collaboration between developers and DevOps teams to efficiently create, update, deploy, run, and manage cloud-based applications.
And some other popular providers are: Microsoft Azure App Service, Google Cloud App Engine, Heroku, Amazon Web Services (AWS) Elastic Beanstalk
What is IaaS?
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is a fundamental cloud computing service model that provides virtualized computing resources over the Internet. In IaaS, a third-party provider hosts and maintains the infrastructure, including servers, storage, networking components, and virtualization layers, allowing users to access these resources on demand. IaaS provides the core building blocks required to execute programs and manage data on the cloud.
Features and benefits of IaaS
Scalability
IaaS offers horizontal and vertical scalability, allowing users to scale resources up or down based on demand. This ensures optimal performance during peak times while saving costs during periods of low usage.
Cost-Effectiveness
IaaS uses a pay-as-you-go model to reduce the need for upfront infrastructure investments. Users just pay for the resources they use, lowering total IT costs.
Flexibility and Customization
IaaS allows users to select specific hardware configurations, operating systems, and software, allowing them to customize the infrastructure to their individual needs.
Disaster Recovery and Backup
IaaS allows users to select specific hardware configurations, operating systems, and software, allowing them to customize the infrastructure to their needs.
Global Reach
With data centers worldwide, IaaS enables businesses to deploy applications closer to their target audience, reducing latency and improving user experience.
Use cases for Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Development and Testing Environments: IaaS is ideal for creating temporary development and testing environments, allowing teams to set up and tear down resources as needed quickly.
- Web Hosting and E-commerce: IaaS provides a reliable and scalable infrastructure for hosting websites and e-commerce platforms, accommodating fluctuations in traffic.
- Big Data and Analytics: Handling vast amounts of data requires significant computing power and storage, which IaaS can efficiently provide.
- Disaster Recovery: IaaS facilitates creating off-site backup environments for disaster recovery, ensuring data safety and availability.
- Software Development: IaaS allows developers to focus on coding and application logic, leaving infrastructure management to the service provider.
Top Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) providers
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): One of the leading IaaS providers, offering a vast array of services and global data center locations.
- Microsoft Azure: Microsoft's cloud platform, providing a comprehensive set of IaaS offerings and seamless integration with other Microsoft services.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP): Google's IaaS solution, is known for its data analytics capabilities and machine learning services.
- IBM Cloud: IBM's cloud infrastructure service, caters to enterprise-level workloads while emphasizing security and hybrid cloud integration.
- DigitalOcean: A user-friendly IaaS provider that is especially popular among developers and startups due to its ease of use and low cost.
What is SaaS?
Software as a Service (SaaS) is a cloud computing service model that delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. Unlike traditional software, where users must install and maintain applications on their local devices, SaaS allows users to access and use software through a web browser. The software is hosted and maintained by a third-party provider, relieving users of the burden of software management, updates, and infrastructure maintenance.
Features and benefits of SaaS
Cost-Effectiveness
SaaS eliminates the need for purchasing, installing, and maintaining software locally, reducing upfront costs and IT overhead.
Scalability
Users may simply scale up or down their software consumption based on changing demands without worrying about hardware upgrades or capacity planning.
Accessibility and Collaboration
SaaS applications can be accessed from anywhere, fostering collaboration among teams and individuals working remotely.
Automatic Updates and Maintenance
SaaS providers handle software updates, maintenance, security, and backups, ensuring optimal performance and data integrity.
Quick Deployment
With no need for installation, users can use SaaS applications almost instantly, accelerating time-to-value.
Different Types of Business Software as SaaS Applications
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
SaaS-based CRM platforms allow businesses to efficiently manage customer interactions, sales pipelines, and marketing campaigns.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
SaaS ERP solutions streamline and integrate core business processes like finance, HR, and inventory management.
Collaboration and Productivity
SaaS tools like office suites, project management, and communication apps enhance team collaboration and productivity like Cloud Ai-WAF, and MailCloud.
Human Resources Management (HRM)
SaaS HR platforms assist with recruitment, employee onboarding, payroll processing, and performance management.
Marketing Automation
SaaS marketing tools enable businesses to automate and optimize their marketing efforts across various channels.
Most Popular SaaS Application Examples
- Salesforce: A leading SaaS provider offering a robust CRM platform used by businesses of all sizes worldwide.
- Microsoft 365 (formerly Office 365): Microsoft's suite of cloud-based productivity tools, including Word, Excel, Outlook, and Teams.
- Google Workspace (formerly G Suite): Google's SaaS offering comprises productivity tools like Gmail, Docs, Sheets, and Drive.
- Slack: A popular SaaS-based team communication and collaboration platform.
- Zoom: A widely used SaaS video conferencing and virtual meeting solution.
IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS: What's the difference?
Cloud computing has transformed how businesses and individuals access and utilize computing resources and software applications. Three primary cloud service models have emerged: Platform as a Service (PaaS), Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). This comprehensive guide aims to compare these models and help you understand their advantages and disadvantages and how to choose the most suitable service model for specific needs.
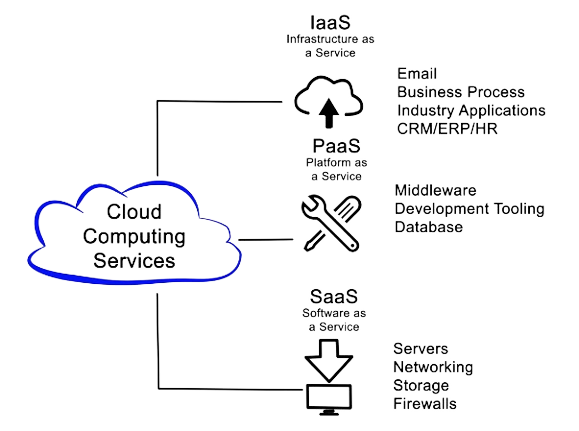
Difference between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
| Basis Of | IaaS | PaaS | SaaS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stands for | Infrastructure as a Service | Platform as a Service | Software as a Service |
| Use cases | Network architects | Developers | The end user |
| Access | IaaS delivers virtualized resources, encompassing virtual machines and storage functionalities. | PaaS provides application deployment and development tools with access to a runtime environment. | SaaS provides the end user with access. |
| Model | Provides virtualized computing resources accessible via the Internet. | Provides application development tools. | Hosts software, making it readily available to clients. |
| Technical understanding | It requires technical knowledge. | Basic knowledge is required for the initial setup. | There is no requirement for technicalities company handles everything. |
| Popularity | It is popular among developers and researchers. | It is popular among developers who focus on developing apps and scripts. | It is popular among consumers and companies, including file sharing, email, and networking. |
| Usage | Skilled developers leverage it to create one-of-a-kind applications. | Used by mid-level developers to build applications. | Used among the users of entertainment. |
| User Manage | Platform ( Operating System, Runtime, Middleware, and Application Data | Data of the application | Nothing |
| Disadvantages | 1.Management Overhead: Users are responsible for managing and maintaining virtual machines, requiring some IT expertise. 2. Potential Resource Overprovisioning: Users may pay for unused resources without careful monitoring. |
1. Platform Lock-in: Selecting a specific PaaS may limit the portability of applications to other platforms. 2. Limited Control: Users have less control over the underlying infrastructure, which may restrict specific customization options. |
1. Limited Customization: Users may have limited control over software configurations and features, depending on the SaaS provider. 2. Data Security Concerns: storing sensitive data on third-party servers may raise security and compliance concerns for specific industries. |





